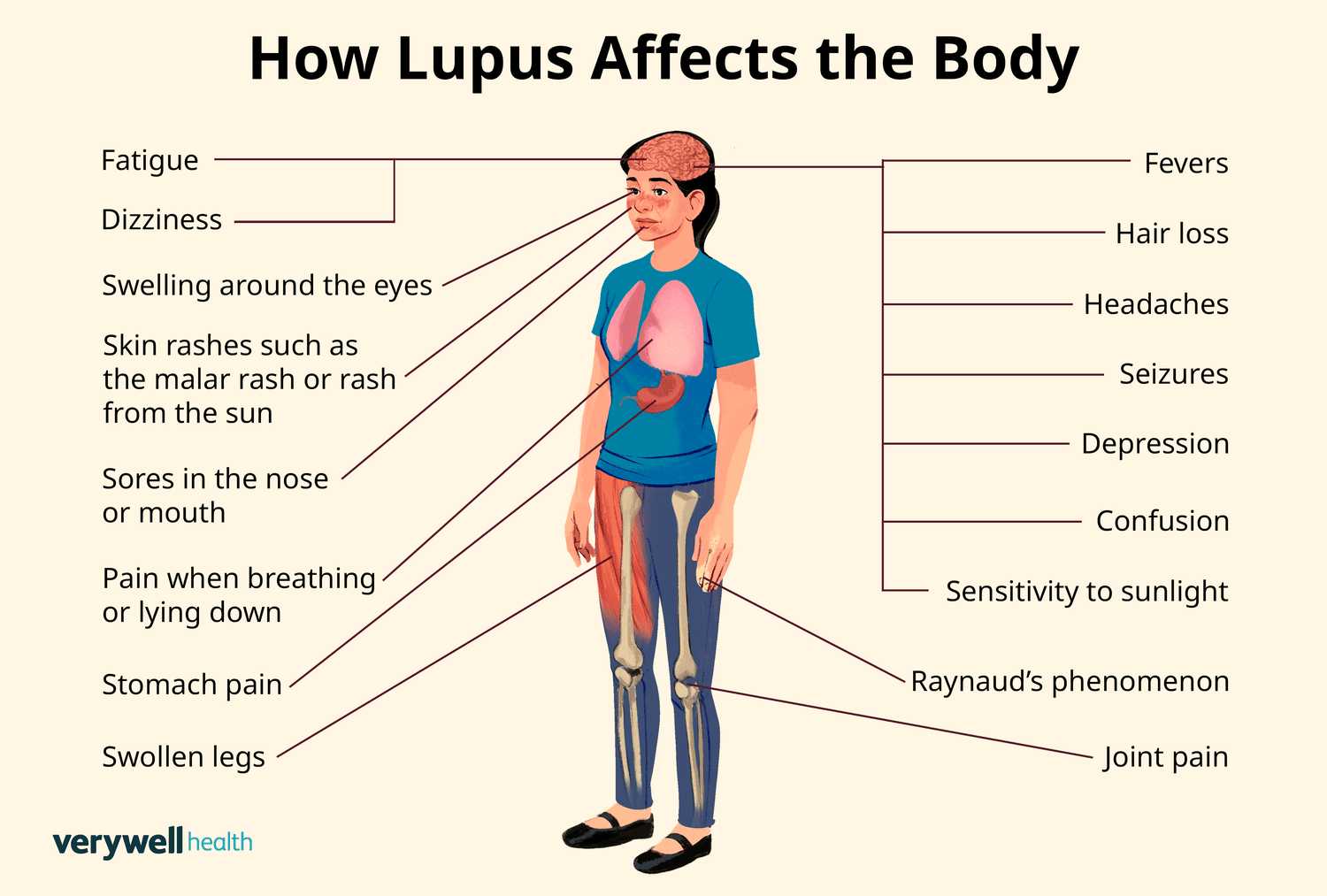
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide, often in a debilitating manner. While many individuals with lupus lead normal, fulfilling lives with the right treatment and management, the disease can cause severe complications that may put a person’s life at risk. This raises the important question: Can lupus kill you? In this blog, we will explore the severity of lupus complications, the factors that contribute to life-threatening situations, and how to manage these risks effectively to improve the quality of life for those affected by lupus.
What is Lupus?
Lupus, specifically systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs. The immune system, which is designed to protect the body from infections, becomes hyperactive and attacks normal cells, leading to inflammation and damage in various parts of the body. Lupus can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and other organs, and its impact can range from mild to severe.
The cause of lupus is still not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. It is more common in women, particularly those of childbearing age, and tends to be more prevalent in people of African American, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American descent.
Can Lupus Be Fatal?
While lupus itself is not directly fatal, it can lead to life-threatening complications that increase the risk of mortality. The severity of lupus and its complications vary greatly from person to person, and early diagnosis, proper treatment, and regular monitoring can help reduce the risks.
For some individuals, lupus can progress to the point where it significantly affects vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, and lungs. If these organs become severely damaged, they can fail, which could ultimately lead to death. The key to reducing the risk of life-threatening complications is understanding the various ways lupus can progress and how to manage these risks.
Lupus Complications: How Can Lupus Be Life-Threatening?
Several lupus complications can contribute to a life-threatening situation. Some of the most common and severe complications include:
1. Kidney Damage (Lupus Nephritis)
One of the most serious complications of lupus is lupus nephritis, a condition where the kidneys become inflamed and damaged. This can impair their ability to filter waste products and excess fluids from the body, leading to kidney failure. Lupus nephritis affects approximately 40% of individuals with lupus, and when left untreated, it can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
The severity of lupus nephritis can be monitored through regular blood and urine tests. Treatment typically involves immunosuppressive medications, corticosteroids, and sometimes other drugs that target specific aspects of the immune system. When diagnosed early and treated properly, many people with lupus nephritis can manage the condition and avoid kidney failure.
2. Heart Disease and Stroke
Lupus significantly increases the risk of developing heart disease and having a stroke. The inflammation caused by lupus can damage the blood vessels and increase the likelihood of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up inside the arteries, restricting blood flow. This can lead to coronary artery disease (CAD), heart attacks, and strokes. Lupus patients also have a higher risk of developing pericarditis, which is inflammation of the lining around the heart.
Inflammation can also affect the blood’s ability to clot, increasing the risk of blood clots, which can cause heart attacks, strokes, or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Regular cardiovascular assessments, including blood pressure checks, cholesterol tests, and electrocardiograms (ECGs), are crucial for lupus patients to monitor and manage their heart health.
3. Lung Involvement
The lungs can be affected by lupus in several ways, including pleuritis (inflammation of the lining around the lungs) and interstitial lung disease (lung scarring). Both conditions can cause chest pain, difficulty breathing, and long-term lung damage. In severe cases, lung damage can be life-threatening and may require treatments such as oxygen therapy, immunosuppressive medications, or even a lung transplant in the most extreme cases.
4. Infections and Immune System Suppression
Lupus itself can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Additionally, the medications used to treat lupus, particularly immunosuppressive drugs, can further weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Common infections that may become life-threatening for lupus patients include pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections.
Infections can be managed by promptly addressing symptoms and seeking medical care when needed. Preventative measures, such as regular vaccinations and practicing good hygiene, can also help reduce the risk of infections.
5. Blood Clots and Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Lupus increases the risk of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), a condition where the blood becomes prone to clotting. APS can lead to serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or stroke. Individuals with both lupus and APS may need blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) to prevent dangerous clots from forming.
How to Manage the Risks of Lupus
While lupus complications can be life-threatening, the risk of severe outcomes can be significantly reduced with proper management. Here are several strategies for managing lupus and minimizing life-threatening risks:
1. Early Diagnosis and Monitoring
Early diagnosis is crucial in reducing the risk of severe complications. If lupus is suspected, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider who can perform the necessary tests to confirm the diagnosis. Once diagnosed, regular monitoring of organ function, including kidney function, heart health, and lung health, is essential for catching complications early before they become life-threatening.
2. Medications
The treatment of lupus typically involves a combination of medications designed to suppress the overactive immune system and reduce inflammation. Common medications include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Used to control pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Powerful anti-inflammatory medications that help reduce inflammation and manage flare-ups.
- Immunosuppressive medications: These drugs help suppress the immune system to prevent further damage to organs.
- Antimalarial drugs: Hydroxychloroquine is commonly prescribed to control skin and joint symptoms.
- Blood thinners: For individuals with antiphospholipid syndrome, anticoagulants can help prevent blood clots.
Adhering to the prescribed medication regimen and working closely with a healthcare team to monitor the effectiveness of treatment is crucial for managing the disease and reducing the risk of complications.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with lupus. Here are some important lifestyle tips:
- Protecting from the sun: Since sun exposure can trigger lupus flare-ups, wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding direct sunlight during peak hours is important.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help maintain overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve joint function, boost energy levels, and enhance overall well-being. However, individuals with lupus should avoid overexertion and consult their healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
- Stress management: Stress can trigger lupus flare-ups, so practicing stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness is beneficial.
4. Regular Check-ups
Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for tracking lupus progression and preventing complications. Regular tests, including blood tests, kidney function tests, and cardiovascular assessments, should be performed to detect any emerging issues.
5. Support System
Living with lupus can be challenging, and having a support system is essential. Support from family, friends, and support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional and physical toll of the disease. Talking to others who understand the challenges of living with lupus can provide comfort and practical advice.
Conclusion
The answer to the question, “Can lupus kill you?” is not simple. While lupus itself is rarely fatal, the life-threatening complications that can arise from the disease are significant. Kidney failure, heart disease, strokes, lung damage, and infections are just some of the risks that people with lupus face. However, with early diagnosis, effective treatment, and proactive management, these risks can be minimized, and many individuals with lupus can lead full and productive lives.
If you or someone you know is living with lupus, it is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor and manage the disease. By staying informed about the potential risks and taking steps to mitigate them, you can significantly improve outcomes and enjoy a better quality of life.
Remember, while lupus presents challenges, it does not have to define one’s life. With the right approach, those affected by lupus can live well and thrive.
