Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing red, scaly patches on the skin. While there is no permanent cure, effective psoriasis treatment strategies can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. From medical interventions to natural psoriasis remedies, finding the right approach can make a significant difference. In this guide, we’ll explore various treatment options, including psoriasis medication, home remedies for psoriasis, and lifestyle modifications that can provide relief.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, accelerating their life cycle and causing rapid buildup on the skin’s surface. This leads to inflammation, scaling, and discomfort. While the exact cause is unknown, genetic and environmental factors play a crucial role in triggering the condition.
Common Types of Psoriasis
- Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris): The most common form, characterized by raised, inflamed, and scaly patches. These plaques often appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. They can be itchy, painful, and sometimes crack and bleed.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Small, red, drop-like lesions, often triggered by infections. It is more common in children and young adults and can develop suddenly after a strep throat infection. This type of psoriasis may resolve on its own or develop into chronic plaque psoriasis.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, shiny red lesions in skin folds, such as under breasts or around the groin. The lesions are often irritated by friction and sweating, making them particularly uncomfortable. This type of psoriasis may be resistant to traditional treatments and require specialized care.
- Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules surrounded by inflamed skin, often affecting hands and feet. This type can be localized or widespread, leading to severe discomfort. In some cases, pustular psoriasis may cause flu-like symptoms, including fever and chills.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe, rare form causing widespread redness, shedding, and intense itching or pain. It can be life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. This form of psoriasis can also cause dehydration and fluctuations in body temperature.
Medical Psoriasis Treatment Options
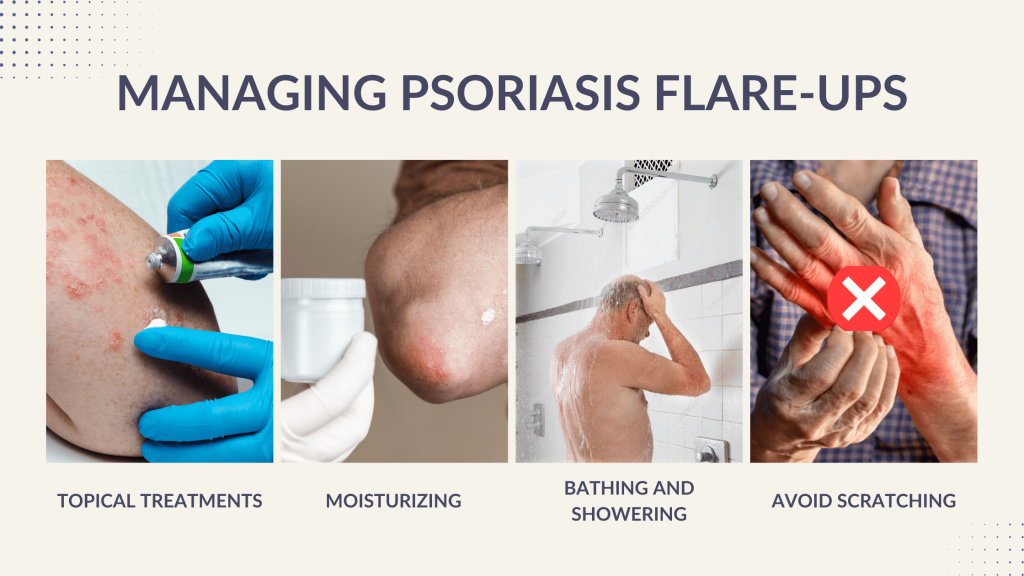
1. Topical Treatments
Topical therapies are often the first line of defense against psoriasis. They help reduce inflammation, slow skin cell growth, and relieve itching.
- Corticosteroids: Commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response. They are available in different strengths, depending on the severity of symptoms. Long-term use of corticosteroids should be monitored by a doctor to avoid skin thinning.
- Vitamin D Analogs (Calcipotriene, Calcitriol): Help slow down skin cell growth and improve symptoms. They work by modulating the immune system’s response. Regular use can reduce plaque thickness and scaling over time.
- Salicylic Acid: Helps remove scales and smooth the skin. It can be found in shampoos, creams, and ointments designed for psoriasis. Salicylic acid is often combined with other treatments to enhance effectiveness.
- Coal Tar: Reduces scaling, itching, and inflammation. Available in different formulations, including shampoos and ointments, it has been used for decades as a psoriasis treatment. Some people may find the smell and staining properties of coal tar unpleasant.
- Topical Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that promote normal skin cell turnover. They help reduce scaling and inflammation but may cause irritation, particularly in sensitive areas. It’s essential to use sunscreen as retinoids can increase sun sensitivity.
2. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation. Common phototherapy options include:
- UVB Therapy: Targets affected areas with controlled UVB light. It is an effective treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis and is often combined with other therapies. Consistency in treatment sessions is crucial for optimal results.
- PUVA Therapy: Combines UVA light with a photosensitizing drug called psoralen. This combination increases the skin’s sensitivity to light, making the treatment more effective. However, long-term PUVA therapy may increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Excimer Laser: Uses concentrated UVB light to treat small patches of psoriasis. It is particularly useful for localized plaques and hard-to-treat areas like the scalp and hands. The treatment is quick and effective but requires multiple sessions.
3. Systemic Treatments (Oral and Injectable Medications)
For moderate to severe cases, systemic medications may be prescribed.
- Biologic Drugs: Target specific immune system components (e.g., adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept). These drugs help reduce inflammation at a molecular level. Biologics are usually administered via injection and require regular monitoring by a healthcare provider.
- Methotrexate: Suppresses the immune system to reduce symptoms. It is often prescribed for severe psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis. Regular liver function tests are necessary as methotrexate can affect liver health.
- Cyclosporine: A powerful immunosuppressant used for severe cases. It provides rapid symptom relief but is not recommended for long-term use due to potential kidney toxicity. Patients on cyclosporine require regular blood pressure and kidney function monitoring.
- Apremilast: A PDE4 inhibitor that helps reduce inflammation. It is taken orally and works by regulating the immune response. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and headache.
Natural Psoriasis Remedies and Home Treatments
While medical treatments are effective, many people seek home remedies for psoriasis to complement their regimen. Natural remedies can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
1. Moisturizing Regularly
Dry skin worsens psoriasis symptoms. Use thick, fragrance-free moisturizers, such as:
- Petroleum jelly: Forms a protective barrier to lock in moisture and reduce irritation.
- Coconut oil: Has anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe psoriasis flare-ups.
- Shea butter: Rich in fatty acids and vitamins that nourish the skin and improve elasticity.
- Aloe vera gel: Provides a cooling effect and helps reduce redness and irritation.
2. Oatmeal Baths
Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can relieve itching and redness. Add colloidal oatmeal to a warm bath and soak for 15-20 minutes. Regular oatmeal baths can help soften scales and promote healing.
3. Dead Sea Salt Soaks
Bathing in warm water with Dead Sea salt can help remove scales and ease irritation. The minerals in Dead Sea salt, such as magnesium and potassium, improve skin hydration and reduce inflammation. Use lukewarm water to prevent excessive drying of the skin.
4. Apple Cider Vinegar
Diluted apple cider vinegar can be applied to the scalp to relieve itching and reduce scaling. It also has antibacterial properties that may help prevent infections in cracked skin. Avoid using it on open wounds to prevent irritation.
5. Turmeric Supplements
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may help manage psoriasis.
6. Dietary Changes
A healthy diet can influence psoriasis severity. Consider:
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Fatty fish, nuts, leafy greens, and berries.
- Avoiding Trigger Foods: Processed foods, red meat, dairy, and alcohol.
- Gluten-Free Diet: Some individuals find symptom relief by eliminating gluten.
Lifestyle Modifications for Psoriasis Management
1. Stress Reduction
Stress is a common psoriasis trigger. Effective stress management techniques include:
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Deep breathing exercises
- Counseling or therapy
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps reduce inflammation, maintain a healthy weight, and improve mental well-being. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and stretching are beneficial.
3. Proper Skincare Routine
- Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
- Avoid hot showers; opt for lukewarm water.
- Pat skin dry instead of rubbing.
- Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing.
4. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen psoriasis symptoms and reduce the effectiveness of treatments.
5. Hydration
Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and support overall health.
When to See a Doctor
If psoriasis symptoms become severe, spread rapidly, or affect daily activities, consult a dermatologist. Professional guidance is essential if:
- Over-the-counter treatments don’t work.
- Symptoms worsen despite treatment.
- Joint pain or swelling develops (potential psoriatic arthritis).
Final Thoughts
Managing psoriasis requires a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and natural psoriasis remedies. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, consistency in treatment and avoiding triggers can significantly improve quality of life. If you’re struggling with psoriasis, work with a healthcare provider to find the best approach for your needs.
By incorporating psoriasis medication, home remedies for psoriasis, and a healthy lifestyle, you can take control of your condition and reduce flare-ups effectively.
