Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Detecting the early signs of RA is crucial for managing symptoms and slowing the disease’s progression. This blog explores the key rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily targets the synovium—the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. Over time, this persistent inflammation can damage cartilage and bones, causing severe pain and loss of function. While RA most commonly affects the hands, wrists, and knees, it can also impact other parts of the body, including the eyes, lungs, and heart.
Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
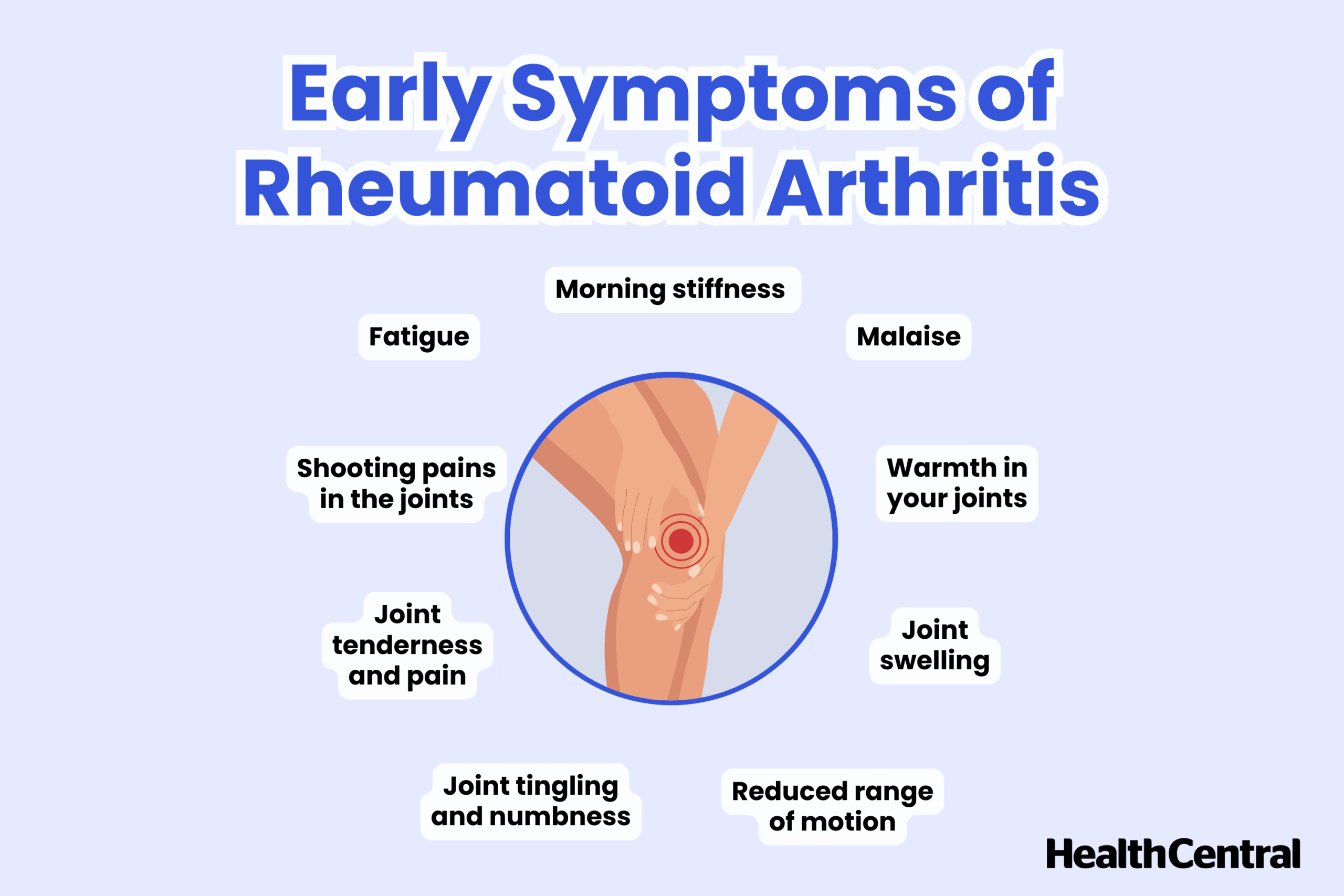
Recognizing the early signs of RA can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively. The sooner RA is diagnosed, the better the chances of controlling inflammation and preventing joint damage. Here are some of the most common early warning signs:
1. Joint Pain and Stiffness
One of the hallmark rheumatoid arthritis symptoms is persistent joint pain, often accompanied by stiffness. This discomfort usually affects multiple joints symmetrically, meaning both sides of the body experience similar symptoms. Stiffness is particularly noticeable in the morning and can last for more than an hour, making everyday tasks challenging.
2. Swelling and Tenderness
Inflammation causes the affected joints to swell, feel tender, and become warm to the touch. Unlike normal swelling from minor injuries, RA-related swelling persists for extended periods and can fluctuate in severity.
3. Fatigue and Weakness
RA is more than just a joint disorder—it also affects overall well-being. Many people with RA experience extreme fatigue, which can be debilitating. This unexplained tiredness often precedes joint symptoms, making it a key early warning sign.
4. Low-Grade Fever
Since RA is an autoimmune disease, the body’s immune response can cause low-grade fevers. If you experience persistent fevers alongside joint pain and fatigue, it may be an indication of an inflammatory condition like RA.
5. Weight Loss and Appetite Changes
Chronic inflammation can lead to unintended weight loss due to a lack of appetite. If you notice significant weight loss without changes in diet or exercise, RA or another autoimmune disorder could be the cause.
6. Numbness and Tingling
RA can compress nerves, leading to sensations of numbness, tingling, or a burning feeling, particularly in the hands and feet. This is often due to inflammation pressing against nerve endings.
7. Reduced Range of Motion
As RA progresses, joint damage can limit flexibility and movement. You might struggle to fully bend or straighten affected joints, making routine tasks like gripping objects, walking, or climbing stairs more difficult.
8. Redness and Warmth in Joints
Inflamed joints may appear red and feel warm due to increased blood flow to the affected areas. This is an important visual indicator of active inflammation.
9. Eye and Mouth Dryness
Some people with RA develop Sjögren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disorder that leads to dry eyes and dry mouth. This occurs when the immune system attacks glands that produce moisture.
10. Chest Pain and Breathing Issues
In severe cases, RA can affect the lungs, leading to inflammation that causes chest pain and breathing difficulties. If you experience shortness of breath or persistent chest discomfort, seek medical attention immediately.
When to See a Doctor
If you are experiencing early signs of RA, consult a healthcare provider as soon as possible. RA is a progressive disease, meaning symptoms will worsen if left untreated. Early diagnosis allows for timely medical intervention, helping to slow joint damage and maintain a better quality of life.
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
A doctor will use several methods to diagnose RA, including:
- Physical examination – Checking for swelling, tenderness, and joint stiffness.
- Blood tests – Measuring inflammation markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibody tests – Identifying autoantibodies linked to RA.
- X-rays and MRI scans – Detecting joint damage and inflammation.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Although there is no cure for RA, several treatment options can help control rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and improve daily functioning. Here’s how to manage RA effectively:
1. Medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – Reduce pain and swelling.
- Corticosteroids – Provide short-term relief from severe inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) – Slow disease progression.
- Biologic agents – Target specific immune system responses to reduce inflammation.
2. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Exercise – Low-impact activities like swimming and yoga improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Healthy Diet – An anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help manage symptoms.
- Stress Management – Practices like meditation and deep breathing exercises can improve mental well-being.
- Adequate Rest – Proper sleep and relaxation techniques help the body recover.
3. Physical Therapy and Assistive Devices
- Physical therapy can strengthen muscles and improve mobility.
- Assistive devices like braces and ergonomic tools can reduce joint strain and improve daily comfort.
4. Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture – May help reduce pain by stimulating nerves.
- Massage therapy – Improves circulation and relieves muscle stiffness.
- Supplements – Omega-3 fatty acids and turmeric have anti-inflammatory properties.
Preventing Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression
While RA cannot be entirely prevented, certain steps can help slow its progression:
- Quit Smoking – Smoking is a major risk factor for RA and worsens symptoms.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight – Excess weight puts extra stress on joints.
- Stay Active – Regular movement helps maintain joint flexibility.
- Monitor Symptoms – Keep track of flare-ups and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong condition, but early detection and proactive management can significantly improve quality of life. Recognizing the rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and seeking timely medical advice can help slow disease progression, reduce pain, and maintain mobility. If you notice persistent joint pain, inflammation, stiffness, or fatigue, consult a doctor for an evaluation. With the right treatment plan, individuals with RA can continue to lead active, fulfilling lives.
By staying informed and making lifestyle adjustments, you can take control of your health and minimize the impact of RA on your daily routine. Don’t ignore the warning signs—act early and prioritize your well-being!
