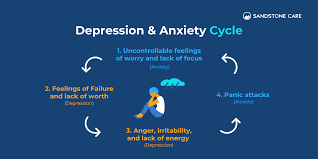
Mixed Anxiety Depressive Disorder (MADD) is a mental health condition that combines symptoms of both anxiety and depression. It presents unique challenges because it encompasses features of both disorders, making it complex to diagnose and treat. Understanding MADD is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies that address its multifaceted nature. This comprehensive guide explores the symptoms of MADD and outlines various treatment options, including both traditional and natural approaches, to help you find the best treatment for depression.
Understanding Mixed Anxiety Depressive Disorder
Mixed Anxiety Depressive Disorder is characterized by the coexistence of anxiety and depressive symptoms, which are present simultaneously but do not meet the criteria for separate diagnoses of anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. This overlap of symptoms can make MADD particularly challenging to identify and treat.
Key Features of MADD
- Simultaneous Symptoms: Individuals with MADD experience symptoms of both anxiety and depression. This can lead to heightened emotional and physical distress, impacting daily functioning and quality of life.
- Duration: Symptoms of MADD must persist for at least six months to be considered for diagnosis. The duration can vary, with some individuals experiencing chronic symptoms while others may have intermittent episodes.
- Functional Impairment: MADD can significantly affect personal, social, and occupational functioning. The combination of anxiety and depression symptoms can make it difficult to maintain relationships, perform at work, or engage in everyday activities.
Symptoms of Mixed Anxiety Depressive Disorder
MADD symptoms can be diverse and may vary in intensity. They generally fall into two main categories: anxiety and depression. Here’s a detailed look at these symptoms:
Anxiety Symptoms
- Excessive Worrying: Persistent, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, or social situations.
- Restlessness: A feeling of being on edge or unable to relax, often accompanied by a sense of impending doom.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness and reduced energy levels, despite adequate rest.
- Muscle Tension: Physical symptoms such as muscle tightness, headaches, and unexplained aches and pains.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling or staying asleep, or experiencing restless and unsatisfying sleep.
Depression Symptoms
- Persistent Sadness: Ongoing feelings of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness that do not seem to improve.
- Loss of Interest: A significant decrease in interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable.
- Changes in Appetite: Significant weight loss or gain due to changes in appetite or eating habits.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and lack of energy, even with adequate rest.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing, making decisions, or remembering things.
Treatment Options for Mixed Anxiety Depressive Disorder
Treating MADD effectively requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both anxiety and depressive symptoms. Here are some of the primary treatment options:
1. Medication
Medication can be an effective part of treatment for MADD, especially when symptoms are severe or resistant to other treatments. Common classes of medications used to treat MADD include:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): SSRIs, such as fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft), are often prescribed for their ability to improve mood and reduce anxiety. They work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain, which helps regulate mood and anxiety.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): SNRIs, like venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta), can help manage both anxiety and depression by increasing levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
- Benzodiazepines: These medications, including diazepam (Valium) and lorazepam (Ativan), are sometimes prescribed for short-term relief of severe anxiety symptoms. However, they are generally not recommended for long-term use due to the risk of dependence.
- Atypical Antidepressants: Medications like bupropion (Wellbutrin) and mirtazapine (Remeron) may be used when other antidepressants are ineffective or cause intolerable side effects.
While medication can be effective, it is often used in conjunction with other treatments, particularly for individuals who have medication-resistant depression or do not respond well to initial medication trials.
2. Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a medication resistant depression treatment of MADD, providing tools and strategies to manage symptoms and improve emotional well-being. Common therapeutic approaches include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is highly effective for treating both anxiety and depression. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety and depression. CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies and problem-solving skills.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): IPT focuses on improving interpersonal relationships and social functioning, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with MADD who struggle with relationship issues or significant life changes.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): MBCT combines cognitive therapy with mindfulness techniques to help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and feelings and reduce the risk of relapse.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT encourages individuals to accept their thoughts and feelings rather than fighting against them. It helps people develop a more flexible and open approach to their emotions and improve their overall well-being.
3. Natural and Complementary Treatments
For individuals seeking alternative or complementary approaches to manage MADD, several natural treatments may offer relief. These can be used alongside conventional treatments or as standalone options for mild symptoms:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity has been shown to improve mood, reduce anxiety, and boost overall well-being. Activities like walking, jogging, or yoga can help alleviate symptoms of both anxiety and depression.
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants can support brain health and improve mood. Foods such as salmon, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are known for their beneficial effects on mental health.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices, including meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation, can help reduce stress and improve emotional regulation.
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbal supplements, such as St. John’s Wort, valerian root, and ashwagandha, have been used to support mood and reduce anxiety. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement, as they can interact with other medications and may not be suitable for everyone.
4. Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating positive lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of MADD:
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a restful environment can help improve sleep quality. This natural treatment for depression is crucial for managing both anxiety and depression.
- Stress Management: Identifying and addressing sources of stress in your life can help reduce the overall burden on your mental health. Techniques such as time management, relaxation exercises, and seeking social support can be beneficial.
- Social Support: Building and maintaining supportive relationships can provide emotional comfort and practical assistance. Engaging in social activities and seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can help combat feelings of isolation.
Seeking Professional Help: Finding a Depression Counselor Near You
Finding a depression counselor near me is an important step in managing MADD effectively. A qualified counselor can provide personalized support and therapy to address both anxiety and depression symptoms. Here are some tips for finding the right counselor:
- Research Credentials: Look for licensed professionals with experience in treating anxiety and depression. Credentials such as Licensed Professional Counselor (LPC), Licensed Clinical Social Worker (LCSW), or Licensed Clinical Psychologist (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) indicate that the counselor has received specialized training.
- Read Reviews: Online reviews and testimonials can offer insights into the experiences of other clients. Look for feedback that highlights the counselor’s effectiveness, empathy, and approach to treatment.
- Consider Compatibility: It’s crucial to find a counselor with whom you feel comfortable and understood. Many counselors offer initial consultations to help you determine if their style and approach are a good fit.
- Check Location and Accessibility: Choose a counselor whose location and availability align with your needs. Consider whether in-person or online sessions would be more convenient for you.
- Evaluate Therapeutic Approach: Different counselors may use various therapeutic techniques. Make sure their approach aligns with your preferences and treatment goals.
Conclusion
Mixed Anxiety Depressive Disorder presents a unique set of challenges due to its combination of anxiety and depressive symptoms. Understanding the symptoms and exploring various treatment options—ranging from medication and psychotherapy to natural and lifestyle approaches—can help you find the most effective strategy for managing this condition. By consulting with a qualified depression counselor near me and considering both conventional and alternative treatments, you can develop a comprehensive plan to address your specific needs and improve your overall well-being.
